















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
The Secrets Beneath Our Feet: Unraveling the Intricate Soil Processes that Impact Water Quality

Our planet is home to a myriad of fascinating and intricate processes that often go unnoticed by the human eye. One such realm lies beneath our very feet – the world of soil. While we may consider soil as nothing more than dirt, it plays a pivotal role in shaping our environment and, particularly, the quality of our water.
In recent years, advances in soil science have shed light on the interconnected relationship between soil processes and water quality. Scientists have unraveled the intricate web of mechanisms that influence the movement of water through soil, the filtration of pollutants, and the overall health of our ecosystems.
Understanding Soil Processes
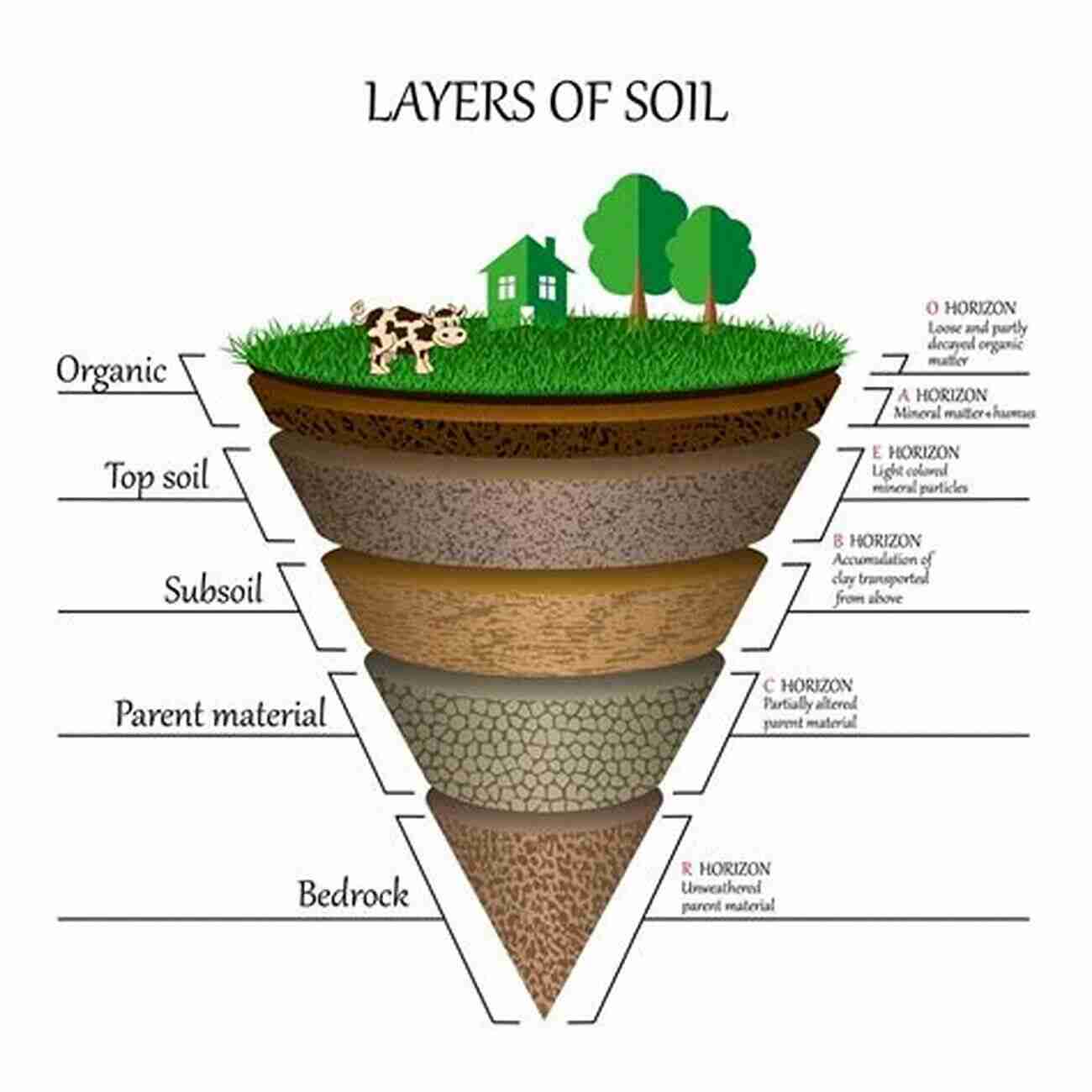
Soil is a complex mixture of minerals, organic matter, gases, liquids, and organisms. It serves as the foundation for terrestrial life, providing nutrients to plants, supporting microbial communities, and regulating the water cycle.
4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 61300 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 416 pages |
One of the fundamental processes that shape soil is weathering. Over millennia, rocks break down due to physical, chemical, and biological processes, yielding the diverse array of minerals found in soils. Weathering also contributes to the soil's ability to absorb and retain water.
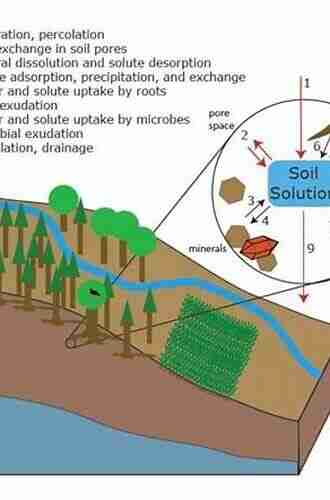
Infiltration, the process by which water enters the soil, plays a critical role in water quality. When rainwater reaches the ground, it infiltrates through the soil, carrying with it various pollutants such as fertilizers, pesticides, and sediment. The ability of soil to filter these contaminants or allow them to percolate into groundwater depends on its composition and structure.
Advancements in Soil Science
The field of soil science has witnessed remarkable advancements in recent decades, with scientists employing innovative techniques to unravel the intricacies of soil processes.
One such breakthrough is the use of remote sensing technologies to map and monitor soil moisture content. By analyzing satellite images and ground-based sensors, researchers can obtain accurate data about the water content in the soil, allowing for informed decisions regarding irrigation practices and crop management.
Furthermore, the emergence of genetic sequencing techniques has revolutionized our understanding of microbial communities in soil. Microbes, such as bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and pollutant degradation. By sequencing their genetic material, scientists can identify key players in these processes, paving the way for targeted interventions to improve soil health.
The Impact on Water Quality
The intricate web of soil processes directly impacts water quality, particularly in agricultural landscapes where intensive farming practices can lead to water pollution. Understanding these processes is crucial for mitigating the adverse effects of agriculture on water resources.
Soil erosion, a significant concern in agroecosystems, can result in sediment and nutrient runoff entering nearby water bodies. Excessive fertilizer application contributes to the build-up of nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, in the soil. During rainfall or irrigation events, these nutrients can be transported to rivers and lakes, leading to eutrophication – a process that causes excessive algal growth, oxygen depletion, and overall degradation of aquatic ecosystems.
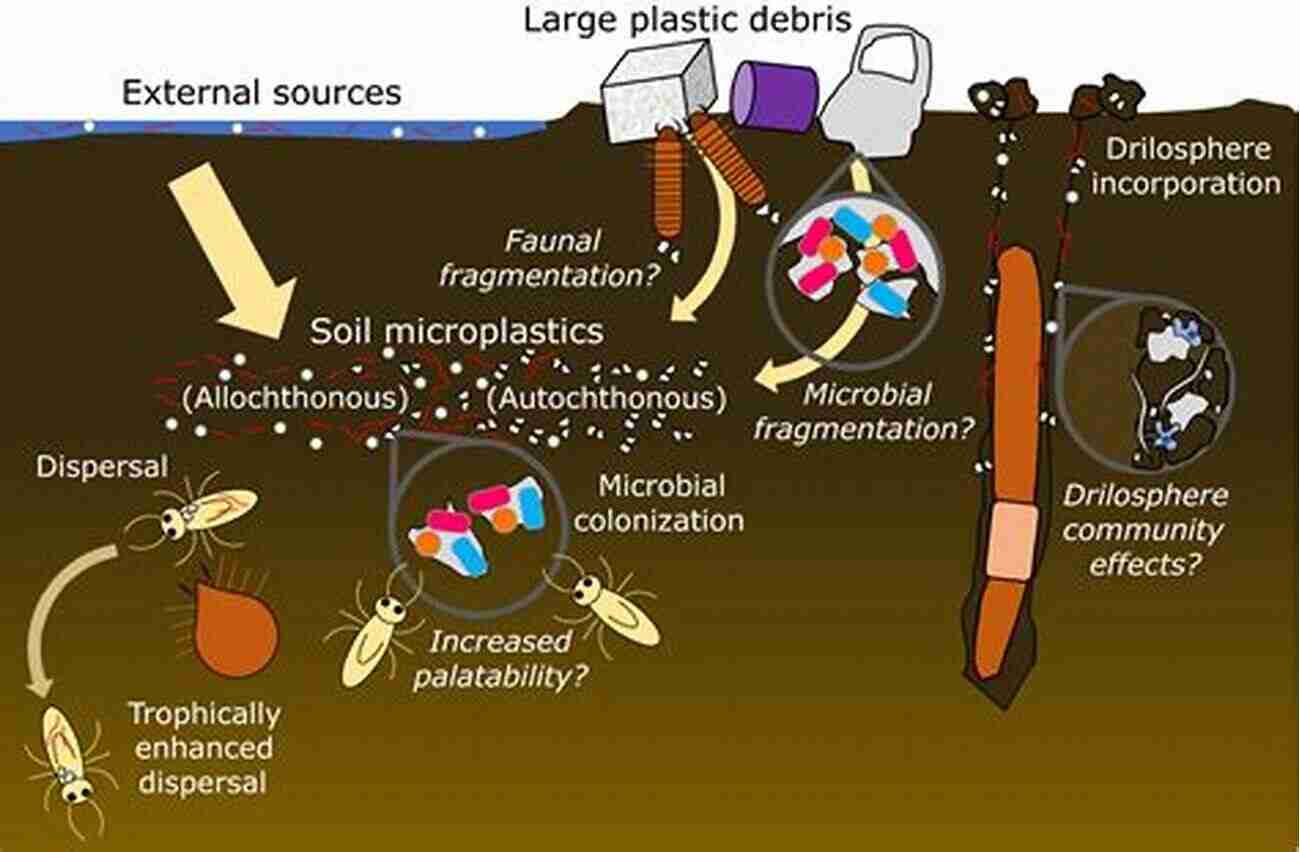
Another vital soil process that affects water quality is the degradation and attenuation of pollutants. Certain soil properties, such as high organic matter content and specific soil microorganisms, have the ability to break down and immobilize pollutants, preventing them from reaching groundwater or nearby surface waters.
Best Management Practices
Given the essential role of soil processes in water quality, adopting best management practices (BMPs) is crucial for sustainable land and water management.
Implementing soil conservation practices, such as contour plowing, cover cropping, and terracing, can significantly reduce soil erosion and the associated water pollution. These practices help retain soil moisture, enhance soil structure, and promote the growth of beneficial microbial communities.
Optimizing nutrient management is also essential to preserve water quality. Precision agriculture techniques, including variable rate fertilizer application and site-specific nutrient management, allow farmers to apply fertilizers in a targeted manner, based on the soil's nutrient needs. This approach minimizes the risk of nutrient runoff and subsequent water contamination.
The Future of Soil Science and Water Quality
The advancements in soil science have opened up exciting possibilities for preserving water quality in a rapidly changing world. By deepening our understanding of soil processes, scientists can develop innovative mitigation strategies, assess the risks associated with pollutants, and establish sustainable management practices.
Investing in soil health research and education is paramount to provide the knowledge and tools necessary for addressing water quality challenges. By fostering interdisciplinary collaborations, we can unlock the secrets beneath our feet and ensure a more sustainable future for our precious water resources.

4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 61300 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 416 pages |
Agrochemicals and agricultural practices have a tremendous impact on environmental quality, particularly their role in water quality degradation. Soil Processes and Water Quality examines principles and practices that minimize the risks of water pollution while enhancing agricultural intensification and productivity. It focuses on how agricultural practices-such as tillage methods, use of fertilizers and manures, cropping systems, and the use of agrochemicals and pest control measures-impact soil processes and affect water quality. Extensive coverage of such topics as water contamination by runoff, leaching, macropore flow, and sediments is also included.
Rapid increases in the use of agrochemicals make Soil Processes and Water Quality an indispensable reference for soil scientists, water quality professionals, researchers, environmental chemists, agrochemicals professionals, government agency employees, academic instructors, agronomists, and students.

 Howard Powell
Howard PowellUnmasking the Enigma: A Colliding World of Bartleby and...
When it comes to classic literary works,...

 Jeffrey Cox
Jeffrey CoxCritical Digital Pedagogy Collection: Revolutionizing...
In today's rapidly evolving digital...

 Quincy Ward
Quincy WardThe Diary Of Cruise Ship Speaker: An Unforgettable...
Embark on an incredible...

 Derek Bell
Derek BellBest Rail Trails Illinois: Discover the Perfect Trails...
If you're an outdoor enthusiast looking...

 Adrian Ward
Adrian WardChild Exploitation: A Historical Overview And Present...
Child exploitation is a...

 Camden Mitchell
Camden MitchellThe Untold Story Of The 1909 Expedition To Find The...
Deep within the realms of legends and...

 Spencer Powell
Spencer PowellThrough The Looking Glass - A Wonderland Adventure
Lewis Carroll,...

 Sidney Cox
Sidney CoxAdvances In Food Producing Systems For Arid And Semiarid...
In the face of global warming and the...

 Art Mitchell
Art MitchellThe Devil Chaplain: Exploring the Intriguing Duality of...
When it comes to the relationship between...

 Edgar Hayes
Edgar HayesThe Mists of Time: Cassie and Mekore - Unraveling the...
Have you ever wondered what lies beyond...

 John Steinbeck
John SteinbeckOn Trend: The Business of Forecasting The Future
Do you ever wonder what the future holds?...

 Tim Reed
Tim ReedLove Hate Hotels Late Check Out
Have you ever experienced the joy of...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Leslie CarterThe Ultimate Study Guide for Organic Chemistry 7th Edition: Ace Your Exams...
Leslie CarterThe Ultimate Study Guide for Organic Chemistry 7th Edition: Ace Your Exams...
 George R.R. MartinThe Theory of Habitat Rights for Wild Animals: Exploring Nature's Equity
George R.R. MartinThe Theory of Habitat Rights for Wild Animals: Exploring Nature's Equity
 Enrique BlairThis Mysterious Piece of Mind Will Intrigue You - Unraveling the Secrets of...
Enrique BlairThis Mysterious Piece of Mind Will Intrigue You - Unraveling the Secrets of...
 Julian PowellHow To Start And Operate Your Own Bed And Breakfast: The Ultimate Guide for...
Julian PowellHow To Start And Operate Your Own Bed And Breakfast: The Ultimate Guide for... Jermaine PowellFollow ·8.5k
Jermaine PowellFollow ·8.5k Giovanni MitchellFollow ·12.6k
Giovanni MitchellFollow ·12.6k José SaramagoFollow ·14k
José SaramagoFollow ·14k Gordon CoxFollow ·15.8k
Gordon CoxFollow ·15.8k Shaun NelsonFollow ·4.3k
Shaun NelsonFollow ·4.3k Chance FosterFollow ·2.4k
Chance FosterFollow ·2.4k Willie BlairFollow ·12.7k
Willie BlairFollow ·12.7k Brady MitchellFollow ·9.7k
Brady MitchellFollow ·9.7k