When it comes to ensuring healthy plant growth, macronutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, often take the spotlight. However, micronutrients play a crucial role in plant health and overall productivity. In this article, we will explore the concept of plant micronutrient use efficiency and reveal the secrets to optimizing growth through their effective utilization.
Understanding Plant Micronutrients
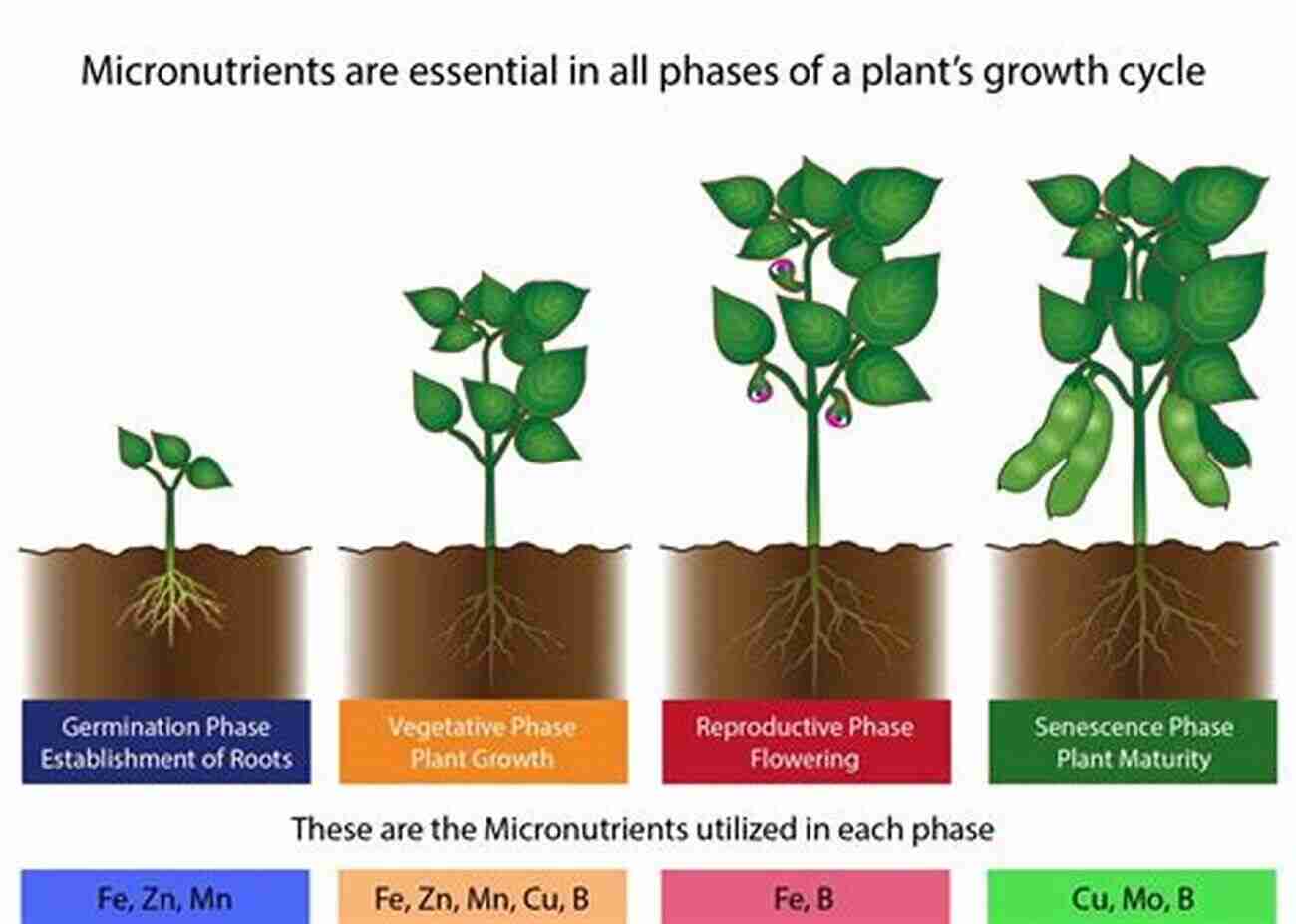
Plant micronutrients refer to essential elements required in small quantities but are equally important for plants' proper development and function. These micronutrients include iron, manganese, boron, copper, zinc, molybdenum, and chlorine. While they are required in trace amounts compared to macronutrients, their absence or deficiency can significantly impact plant health and productivity.
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 17443 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 304 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
The Role of Plant Micronutrient Use Efficiency
Micronutrient use efficiency refers to plants' ability to acquire, translocate, and utilize micronutrients efficiently. Understanding this concept is crucial for enhancing plant growth and productivity while minimizing the negative impacts of deficiencies or excesses. Maximizing plant micronutrient use efficiency requires a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing their availability and uptake.
Factors Influencing Micronutrient Availability
Several factors determine the availability of micronutrients in soil or growing media. Soil pH plays a critical role, as it affects the solubility and mobility of different micronutrients. Additionally, soil organic matter content, cation exchange capacity, and the presence of other minerals can influence the availability of micronutrients to plants. A thorough soil analysis can help identify potential deficiencies or imbalances.
Micronutrient Uptake and Translocation
Once micronutrients are available in the soil, plants need to efficiently uptake and transport them to the sites of demand. Micronutrient uptake involves several processes, including root interception, mass flow, and diffusion. The efficiency of these processes depends on factors such as root morphology, soil moisture content, root exudates, and the concentration of other nutrients in the soil solution.
Enhancing Plant Micronutrient Use Efficiency
Achieving optimal plant growth and yield requires strategies to enhance micronutrient use efficiency. One approach is through proper soil management practices, including pH adjustment, maintaining organic matter levels, and balancing nutrient ratios. The use of chelated micronutrient fertilizers can also improve availability and uptake. Another strategy is foliar application, which bypasses potential soil limitations and ensures direct access to plants' nutrient demands.
Plant micronutrient use efficiency is a critical factor in achieving optimal growth and productivity. By understanding the factors influencing availability and uptake, and implementing appropriate management practices, growers can unlock the secrets to maximizing plant micronutrient use efficiency. With careful attention to these essential elements, plants can thrive and reach their full potential.