















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Mechanism Underlying The Resistance To Prion Diseases Focus On Structural

Prion diseases are a group of neurodegenerative disorders characterized by the accumulation of abnormal prion proteins in the brain. These proteins can convert normal proteins into the abnormal form, leading to the formation of insoluble aggregates that disrupt normal cellular functions. Despite the potential severity of prion diseases, some individuals display a natural resistance to their development. Understanding the mechanisms underlying this resistance can provide valuable insights into potential therapeutic interventions.
Structural Features
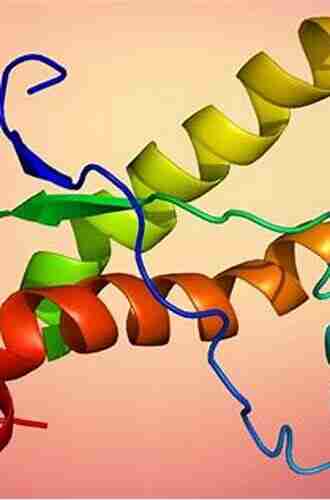
The resistance to prion diseases is largely attributed to certain structural features of the prion protein that make it more difficult for abnormal conformational changes to occur. One such feature is the presence of specific amino acid sequences within the protein structure that impede the conversion process. These sequences act as roadblocks or steric hindrances, preventing the abnormal prion proteins from adopting the conformation necessary for propagation.
Additionally, the resistance can be influenced by the stability of the protein structure. Prion proteins with a higher degree of stability are less prone to misfolding and aggregation. This stability can be attributed to a variety of factors, including hydrogen bonding patterns, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bonds. By maintaining a stable conformation, the prion protein is less likely to undergo the structural changes required for disease progression.
4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 26095 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 690 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors also play a significant role in the resistance to prion diseases. Certain variations in the prion protein gene (PRNP) have been associated with a decreased susceptibility to prion infection. These genetic variations can lead to alterations in the protein structure, affecting its ability to undergo the abnormal conformational change. Studying these genetic variants and their impact on prion resistance can help identify potential targets for therapeutic interventions.
Furthermore, the expression levels of cellular factors involved in the prion propagation process can influence the resistance to prion diseases. Cells with higher levels of chaperone proteins, such as heat shock proteins, have been found to exhibit increased resistance to prion infection. These chaperones assist in protein folding and prevent the accumulation of misfolded proteins. Understanding the regulation of these cellular factors and their role in prion resistance can provide valuable insights into therapeutic strategies.
Immunological Responses
The immune system also plays a crucial role in determining the resistance to prion diseases. The activation of innate and adaptive immune responses can limit the spread and accumulation of abnormal prion proteins in the brain. Microglial cells, the resident immune cells in the central nervous system, play a vital role in the clearance of prion aggregates. These cells can recognize and phagocytose abnormal proteins, preventing their accumulation and spread to neighboring cells.
Additionally, the production of specific antibodies against prion proteins can contribute to the resistance against prion diseases. These antibodies can neutralize the toxic effects of the abnormal prion proteins, preventing their interaction with normal proteins. The development of therapeutic antibodies targeting prion proteins is an area of active research and holds promise for future treatment options.
The resistance to prion diseases involves a complex interplay between structural, genetic, and immunological factors. Understanding the mechanisms underlying this resistance provides valuable insights into potential therapeutic interventions aimed at preventing or treating prion diseases. Further research is required to unravel the intricate details of prion resistance and translate these findings into effective clinical strategies.
4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 26095 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 690 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
This monograph is the first easy-to-read-and-understand book on prion proteins' molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and on prions' molecular modelling (MM) constructions. It enables researchers to see what is crucial to the conformational change from normal cellular prion protein (PrPC) to diseased infectious prions (PrPSc),using MD and MM techniques. As we all know, prion diseases, caused by the body's own proteins, are invariably fatal and highly infectious neurodegenerative diseases effecting humans and almost all animals for a major public health concern. Prion contains no nucleic acids and it is a misshapen or conformation-changed protein that acts like an infectious agent; thus prion diseases are called “protein structural conformational” diseases.
PrPC is predominant in α-helices but PrPSc are rich in β-sheets in the form as amyloid fibrils; so very amenable to be studied by MD techniques. Through MD, studies on the protein structures and the structural conversion are very important for revealing secrets of prion diseases and for structure-based drug design or discovery. Rabbits, dogs, horses and buffaloes are reported to be the few low susceptibility species to prion diseases; this book's MD studies on these species are clearly helpful to understand the mechanism underlying the resistance to prion diseases. PrP(1-120) usually has no clear molecular structures; this book also studies this unstructured region through MD and especially MM techniques from the global optimization point of view.
This book is ideal for practitioners in computing of biophysics, biochemistry, biomedicine, bioinformatics, cheminformatics, materials science and engineering, applied mathematics and theoretical physics, information technology, operations research, biostatistics, etc. As an accessible to these fields, this book is also ideal as a teaching material for students.

 Howard Powell
Howard PowellUnmasking the Enigma: A Colliding World of Bartleby and...
When it comes to classic literary works,...

 Jeffrey Cox
Jeffrey CoxCritical Digital Pedagogy Collection: Revolutionizing...
In today's rapidly evolving digital...

 Quincy Ward
Quincy WardThe Diary Of Cruise Ship Speaker: An Unforgettable...
Embark on an incredible...

 Derek Bell
Derek BellBest Rail Trails Illinois: Discover the Perfect Trails...
If you're an outdoor enthusiast looking...

 Adrian Ward
Adrian WardChild Exploitation: A Historical Overview And Present...
Child exploitation is a...

 Camden Mitchell
Camden MitchellThe Untold Story Of The 1909 Expedition To Find The...
Deep within the realms of legends and...

 Spencer Powell
Spencer PowellThrough The Looking Glass - A Wonderland Adventure
Lewis Carroll,...

 Sidney Cox
Sidney CoxAdvances In Food Producing Systems For Arid And Semiarid...
In the face of global warming and the...

 Art Mitchell
Art MitchellThe Devil Chaplain: Exploring the Intriguing Duality of...
When it comes to the relationship between...

 Edgar Hayes
Edgar HayesThe Mists of Time: Cassie and Mekore - Unraveling the...
Have you ever wondered what lies beyond...

 John Steinbeck
John SteinbeckOn Trend: The Business of Forecasting The Future
Do you ever wonder what the future holds?...

 Tim Reed
Tim ReedLove Hate Hotels Late Check Out
Have you ever experienced the joy of...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Jared PowellDiscover the Power of Structure and Application with Springer Undergraduate...
Jared PowellDiscover the Power of Structure and Application with Springer Undergraduate...
 Casey BellDiscover the Inspiring Speeches of His Majesty Kamehameha IV to the Hawaiian...
Casey BellDiscover the Inspiring Speeches of His Majesty Kamehameha IV to the Hawaiian... Kevin TurnerFollow ·16.1k
Kevin TurnerFollow ·16.1k Andy ColeFollow ·18k
Andy ColeFollow ·18k Richard WrightFollow ·18.9k
Richard WrightFollow ·18.9k Randy HayesFollow ·18.7k
Randy HayesFollow ·18.7k Ray BlairFollow ·7.8k
Ray BlairFollow ·7.8k Darnell MitchellFollow ·10.4k
Darnell MitchellFollow ·10.4k Charles ReedFollow ·5.2k
Charles ReedFollow ·5.2k Michael CrichtonFollow ·8.3k
Michael CrichtonFollow ·8.3k